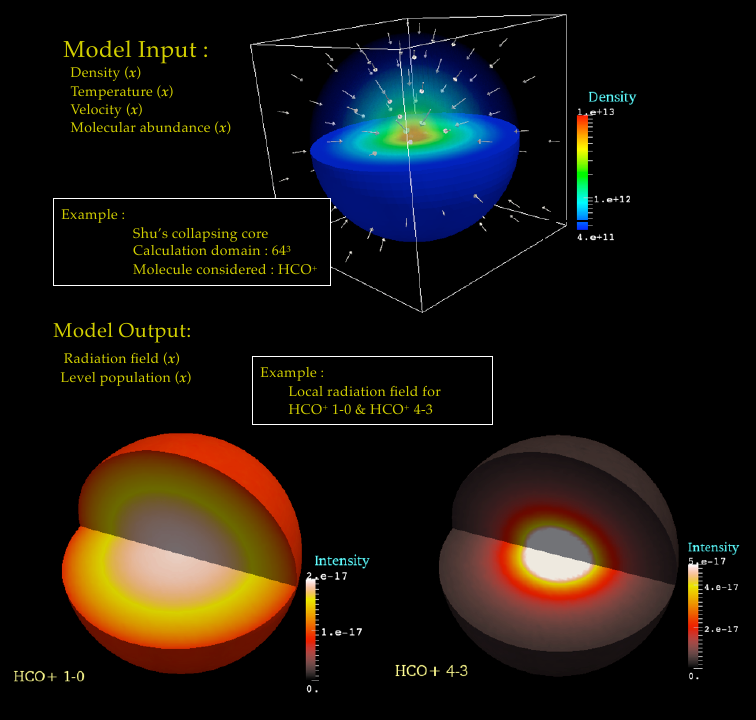
The simulation of SPARX includes the coupling of the global radiative field and local molecular/atomic energy states/excitation. The program requires the input data containing the physical properties such as the distribution of H2 density, kinetic temperature, velocity field, molecular abundance, and dust property
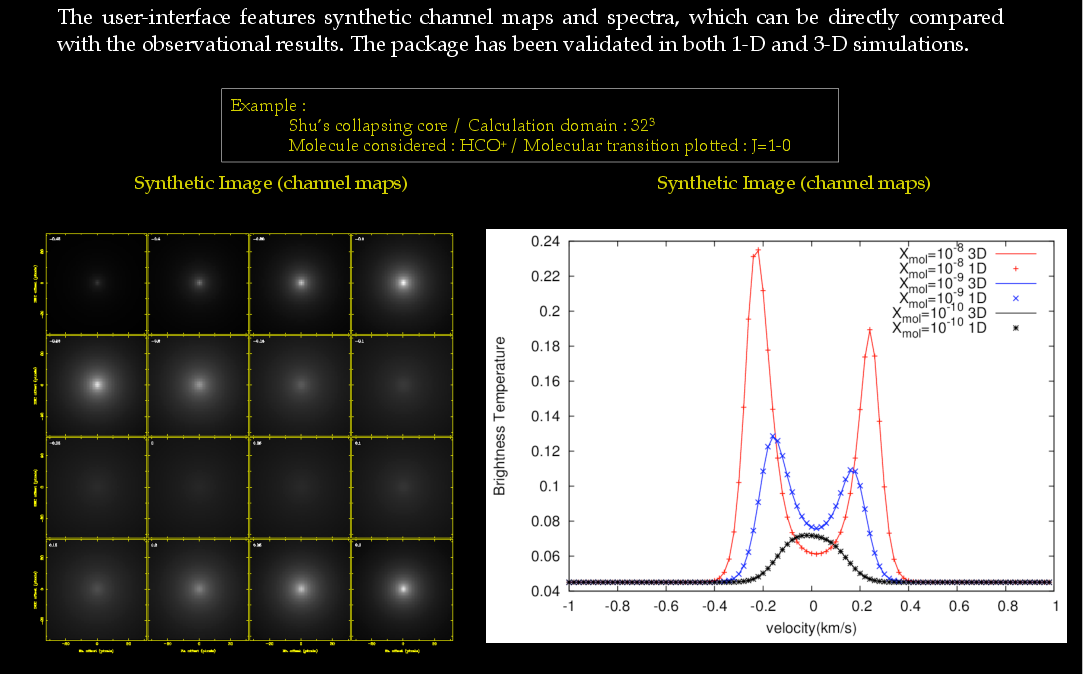
. The outcome of the calculation is the corresponding molecular level populations then their line emission could be synthesized and compared to the format of the real observation.
Mathematical Modeling
For the radiative modeling, the package solves radiative transfer equation (RTE), of which the differential form is
![]()
αν is the absorption coefficient and jν is the emission coefficient. For the other form
![]()
Where increase of the optical depth dτν = ανds , and the source function Sν = jν / αν
We consider the integral form of RTE for the finite cells, the emission from a homogeneous finite element, in which it has the uniform physical quantities, is
![]()
The mean intensity is defined as
![]()
The Doppler broadening function is
![]()
b is the line width summed by turbulent dispersion and thermal speed.
The equation of statistical equilibrium about the molecular levels considers molecular self-emission, stimulated emission, and the collision with the gas particles. The formulation becomes
![]()
The emission coefficient and the absorption coefficient relate with Einstein A and Einstein B coefficients
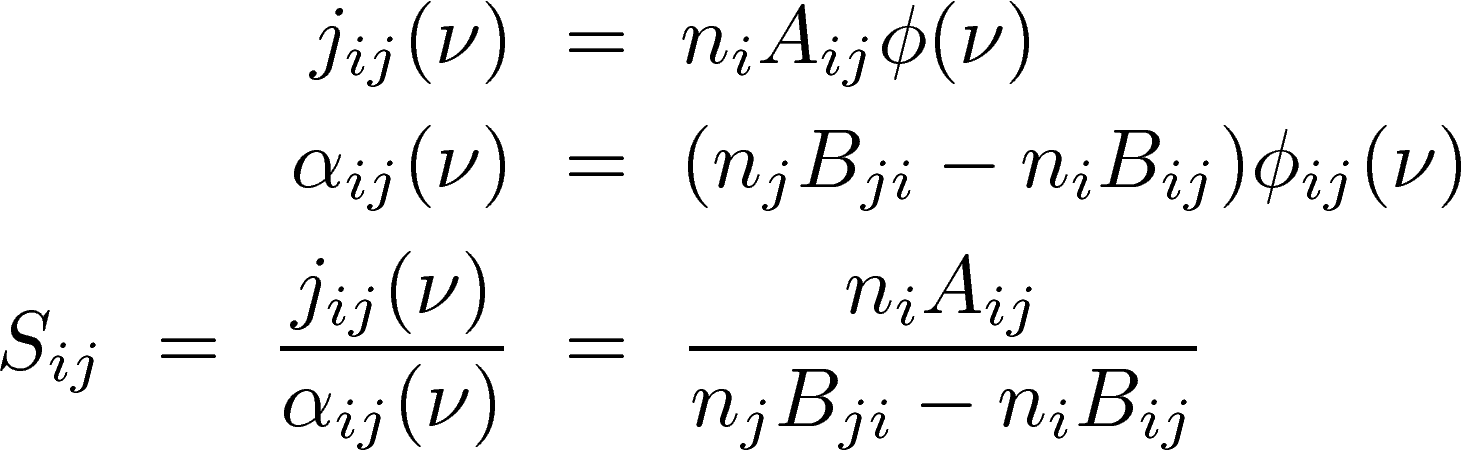
Free-free emission
The absorption coefficient in H II region is adopted from the equation in Gordon’s book “Radio Recombination Lines: Their Physics and Astronomical Applications” (2002), P.64, Eq. 2.96
The numerical version of free-free absorption coefficient in CGS unit is
![]()
where ν is in the unit of Hz, Ne and Ni are in the unit of cm-3
Dust Polarization
According to the modeling of the properties of dust grain by Lee, H. M. & Draine, B. T. 1985 (ApJ, 290, 211), the polarized Stokes parameters are
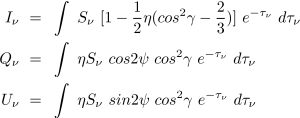
η is the polarized efficiency. And the polarized degree is ![]() , the polarized angle is
, the polarized angle is ![]()
Zeeman splitting
When the molecule is magnetized, its spinning orientation is quantized in the direction of the magnetic field and the transition would be split with the discrete frequency by the splitting factor Z. The photon from the splitting transition has opposite spin thus it turns out a fluctuated Stokes V emission.